Regenerative medicine for COVID treatment may be helpful. The FDA has approved a clinical trial to study COVID-19 patients administered with umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells, which should prevent lung inflammation.


A few days later, after rejecting the diagnosis of seasonal influenza, avian influenza, adenovirus, corona virus, SARS, corona virus, and other pathogens, on Jan. 1, the virus was declared a causative agent of the disease in four of the nine hospitalized patients: A new corona virus that has a 5% genetic association with SARS and is a subset of Sarbecovirus. Currently, the virus has been briefly named SARS-CoV-2 virus for further information and COVID-19, the name was given by the World Health Organization (WHO) to the SARS-CoV-2 virus-associated disease.
Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of COVID-19:

The FDA has approved a clinical trial to study COVID-19 patients administered with umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells, which should prevent lung inflammation. An international team of scientists has been granted immediate US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) authorisation for a 24-patient clinical trial to test the safety and exploratory efficacy of umbilical cord-derived mesenchymal stem cells (UC-MSCs) to prevent the life-threatening lung inflammation that accompanies severe cases of COVID-19. The cell therapy will be managed to patients within a vein.
Stem cell therapy a promising therapeutic field:
Currently, cell-based therapy and especially stem cell therapy has become a promising therapeutic field, in which many opportunities to cure incurable diseases. Despite the significant development of the stem cell-based therapy field, immunogenicity, limited cell source and ethical issue as the main limitations of this therapeutic approach have not been solved yet. Among these, MSCs has attracted attention due to source potential, a high proliferation rate, low invasive procedure, and free of ethical issues. There is much superiority in using MSC therapy in comparison with other treatments.

II) They are multipotent stem cells;
III) MSCs can easily expand to clinical volume in a suitable period of time;
IV) MSCs can be stored for repetitive therapeutic usage;
V) Clinical trials of MSCs so far haven’t shown adverse reactions to allogeneic MSC;
VI) Safety and effectiveness of MSCs have been obviously documented in several clinical trials.
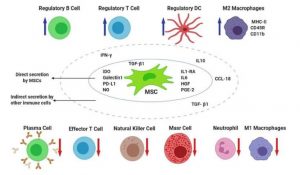
As mentioned, Following the COVID-19, may trigger a destroying immune over reaction in the body. In COVID-19 patients, the immune system produces large amounts of inflammatory factors, causing a cytokine storm including, in an overproduction of immune cells and cytokines. Here, it is the beginning of the MSC therapy idea in the treatment of COVID-19 patients. Probably, MSC therapy can prevent the storm release of cytokines by the immune system and promote endogenous repair by reparative properties of the stem cells.
MSCs-based therapy an ideal candidate for clinical trials:

After intravenous injection, part of the MSC population entraps in the lung, which often in systemic infusion it is remembered as a limitation. Nevertheless here these MSCs could improve respiratory micro environment, interrupt pulmonary fibrosis, defend alveolar epithelial cells and treatment for lung dysfunction and inflammation due to COVID-19. However, one of the main restrictions in this approach is the supplying source of clinical-grade MSCs and subsequently the speed of preparation for clinical usage that stem cell banks can play an important role. Also, MSCs can be isolated from different adult tissues, including preferably bone marrow (BM), peripheral blood (PB) and adipose tissues (AT) (such as abdominal fat, infrapatellar fat pad, and buccal fat pad) and neonatal birth-associated tissues, including placenta (PL), umbilical cord (UC), Warton jelly (WJ), amniotic fluid (AF), and cord blood (CB), and then stored for future possible applications.
Therefore, it seems MSCs-based therapy may possibly be an ideal candidate for clinical trials or at least the combination of treatment to treat COVID-19 patients. Immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties of MSCs in the treatment of respiratory diseases were confirmed by 17 completed clinical studies, and also more than 70 trials are registered in this regard (https://clinicaltrials.gov). To date, 20 clinical trials have been registered in the Chinese clinical trial registry site (http://www.chictr.org.cn). In addition, 9 clinical trials have been registered in Clinicaltrial.gov. Umbilical cord, umbilical cord blood, Wharton’s jelly, menstrual blood, dental pulp, and the company produced-MSCs are the important MSC sources that will be used in these trials. However, the process of developing new therapeutic and bringing it to clinical application has important practical implications and not over for MSC therapy of COVID-19.


Dr. H. Purushothama M.Sc,Phd
Scientist-Regenerative Medicine
Consultant-Nikima Healthcare Solutions
Email: purushothamalab@gmail.com
Mob: 9632175741/9620409055