
Cytokine storm syndromes go by many names, but they share the pathology of an overly active immune response that leads to frequently fatal multi-organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS). The risk factors for why some previously healthy individuals become deathly ill remain unknown. There are likely host factors, including genetic mutations that put individuals at higher risk. Until the risk factors are known, the medical community will need to treat those Covid-19 patients based solely on the severity of their disease.
What are cytokines?
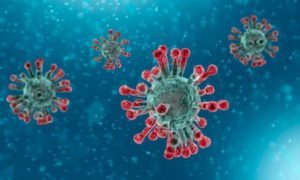

Major types and actions of cytokines:
Type — Actions
1.Interferons- Regulation of innate immunity, activation of antiviral properties, antiproliferative effects
2.Interleukins– Growth and differentiation of leukocytes; many are proinflammatory
3.Chemokines-Control of chemotaxis, leukocyte recruitment; many are proinflammatory
4.Colony stimulating factors-Stimulation of hematopoietic progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation
5.Tumor necrosis factor -Proinflammatory, activates cytotoxic T lymphocytes
What is cytokine storm?
A cytokine storm is an over production of immune cells and their activating compounds (cytokines), which, is often associated with a surge of activated immune cells into the lungs. The resulting lung inflammation and fluid build-up can lead to respiratory distress and can be contaminated by a secondary bacterial pneumonia — often enhancing the mortality in patients.
With the development of biologic therapies for a variety of rheumatic, oncologic, and other conditions, novel approaches to treating the immune response are now available. These highly targeted medicines go after one or a few inflammatory molecules, including cytokines, without the general immune suppression effected by corticosteroids and other relatively non-selective immune suppressants.
Recently, a number of specific anti-cytokine approaches have proven effective in treating a variety of cytokine storm syndromes, including those triggered by viruses. These include drugs targeting interleukin-1 (IL-1), IL-6, IL-18, and interferon-gamma. While randomized trials will be needed to confirm which, if any, of these therapeutics will effectively treat Covid-19-infected patients with cytokine storm syndrome, IL-6 blockade has recently been reported to be in use in China with successful outcomes in some individuals receiving this as part of their treatment.
Pathogenic human Corona virus Infections:
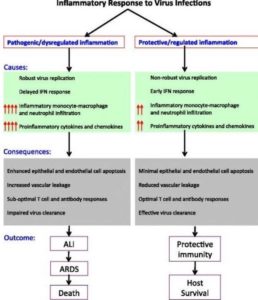

Possible treatment options :
Corticosteroid therapy : Corticosteroids are a class of steroidal hormones that exert anti-inflammatory functions and are generally used to suppress inflammatory conditions.
Interferons : Pegylated and non-pegylated interferons have been under investigation for therapeutic purposes in hCoV-infected individuals.
IFN-αβ inhibitors and IFN-λ : IFN-αβ restrict virus replication through induction of ISGs. However, IFN-αβ can also exacerbate disease by enhancing recruitment and function of inflammatory monocyte-macrophages (IMMs) and other innate immune cells. In contrast to IFN-αβ, IFN-λ mainly activates epithelial cells and lacks monocyte-macrophage-mediated pro-inflammatory activity of IFN-αβ. Additionally, IFN-λ suppresses neutrophil recruitment to the site of inflammation.
Suppression of oxidized phospholipids : Oxidized phospholipids (OxPL) have been shown to promote ALI by increasing lung macrophage cytokine/chemokine production via TLR4-TRIF signaling in influenza A virus (IAV)-infected mice.
Inhibitors of monocyte recruitment and function : Studies in animal models demonstrate pathogenic roles for IMMs during lethal hCoV infections.
Several other immunomodulatory agents that could ameliorate inflammatory responses following pathogenic hCoV infections include cytokine/chemokine inhibitors and danger-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) antagonists. Studies from animal models show a significant contribution of TNF to acute lung injury and impaired T cell responses in SARS-CoV-challenged mice. In vivo neutralization of TNF activity or infection of mice lacking TNFR provides protection against SARS-CoV-induced morbidity and mortality. However, it is to be noted that TNF was not detected in the serum of SARS patients at least during later stages of infection.


Therefore, therapeutic interventions targeting these pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines could prove beneficial in ameliorating undesirable inflammatory responses. Additionally, since high virus titers at early and later stages of infection strongly correlate with disease severity in humans, strategies directed at controlling viral load as well as attenuating the inflammatory response might prove beneficial.


Dr. H. Purushothama M.Sc,Phd
Scientist-Regenerative Medicine
Consultant-Nikima Healthcare Solutions
Email: purushothamalab@gmail.com
Mob: 9632175741/9620409055