What is the treatment for ‘Non-Healing Diabetic Foot Ulcers (DFUs)’? The use of platelet-rich plasma, which is rich in multiple growth factors and cytokines is gaining popularity.
Diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) are among the most common complications of diabetes mellitus with a lifetime incidence of up to 15% among the diabetic population. Studies have shown that up to 80% of patients with DFUs suffer from both limb ischemia and peripheral neuropathy simultaneously. These conditions further delay healing of DFUs, predisposing to higher rates of complications such as Cellu-litis and Osteomyelitis.
In spite of the high prevalence and morbidity associated with DFUs, current treatment options are limited. Current standard management consists of surgical debridement followed by frequent dressing changes with tight infection and glycemic control. Despite this comprehensive approach, complication and amputation rates remain high.
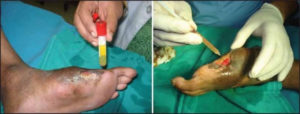

Specifically, the platelet alpha-granules contain several of these molecules, including: platelet derived growth factor (PDGF), TGF-β, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), epithelial growth factor (EGF), fibrinogen, fibronectin, and vitronectin. In addition, platelet delta granules contain serotonin, histamine, dopamine, calcium, and adenosine, which act in tandem with the aforementioned growth factors to regulate wound healing.
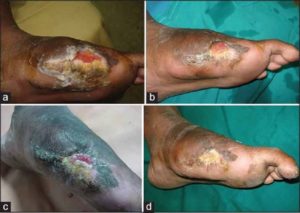

(a) The diabetic left foot ulcer before PRP. (b) After 1 sitting of PRP. (c) Ulcer after four sittings of PRP. (d) Ulcer healed completely at the end of 6 sittings.
For details:


Keshav Ramu
Nikima Health Care Solutions
#63, 4th Cross, VSR Layout
Kanshiramnagara, Bangalore—560097
Mob: 9620409055/9738258780
Email: nikimahealthcare@gmail.com