
What is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)? PCOS is a condition that can affect your periods, fertility, hormones and aspects of appearance. Sometimes it can also affect long-term health. It is estimated widely that 2 to 26 in every 100 women suffer from PCOS.
What are polycystic ovaries?
Polycystic ovaries are slightly larger than normal ovaries and have twice the number of follicles (fluid-filled spaces within the ovary that release the eggs during ovulation). Having polycystic ovaries does not necessarily mean that patient have PCOS. Women with PCOS have symptoms as well as polycystic ovaries.
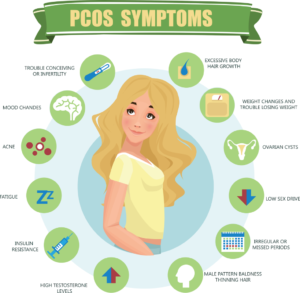
What are the symptoms of PCOS?
- Irregular periods or no periods.
- An increase in facial or body hair (hirsutism).
- Loss of hair on head.
- Being overweight, experiencing a rapid increase in weight or having difficulty losing weight.
- Oily skin, acne.
- Difficulty becoming pregnant (reduced fertility).
- Depression and psychological problems.

What causes PCOS?
The exact cause of PCOS is not yet known, but it often runs in families. We believe that high levels of male hormones prevent the ovaries from producing hormones and making eggs normally. Genes, insulin resistance, and inflammation have all been linked to excess androgen production.
How is PCOS diagnosed?
Women with PCOS often have symptoms that occur irregularly, particularly if their weight has fluctuations. So it is very difficult to diagnose, which means it may take a while to get a diagnosis.
A diagnosis is made when you have any two of the following:
- Irregular, infrequent periods or no periods.
- An increase in facial or body hair and/or blood tests that show higher testosterone levels than normal.
- An ultrasound scan that shows polycystic ovarian morphology.
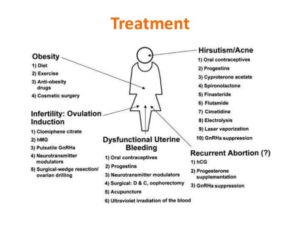
How to treat PCOS?

What could PCOS mean for long-term health?
PCOS patients are at greater risk of developing the long-term health problems like Insulin resistance and diabetes. Patient may develop diabetes during a pregnancy (known as gestational diabetes), obese (a body mass index (BMI) of over 30, high blood pressure, heart problems, depression and mood swings.
What can be done to reduce long-term health risks?
Have a healthy lifestyle. The main ways to reduce overall risk of long-term health problems are:
- Eat a healthy balanced diet.
- Eat meals regularly, especially breakfast.
- Exercise regularly (30 minutes at least three times a week).
- Should aim to maintain normal weight.


Dr. Chaithra S Niranthara
Reproductive Immunology Specialist
Parva diagnostics and health care
Malagala Main Rd, Gangamma Garden
Naagarabhaavi, Bengaluru- 560072
Ph: 063649 11469/ 369