Urinary Tract Infection – A most common type of infection. UTIs are common, but timely diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications. Adopting preventive measures, maintaining good hygiene, and seeking medical attention for recurring cases can contribute to a healthier urinary system.
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection in kidneys, ureters, bladder and urethra, which are the parts of urinary system. It effects especially bladder and the urethra (lower urinary tract). Infection is just painful and annoying until it is limited to bladder, but if it spreads to kidney then it may be chronic.
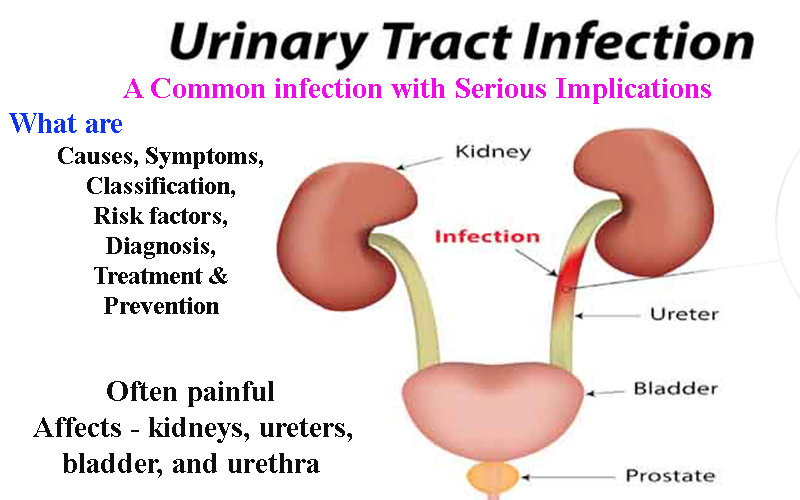

Normally, urine is free of germs or bacteria. After filtering, kidney removes waste products and excess water from the blood in the form of urine, which passes through urinary system. UTI and inflammations occurs if bacteria enter urinary system from outside the body. UTIs are the 2nd most common type of infection. Escherichia coli (E. coli) bacterium causes most UTIs.
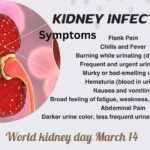
UTI may have some symptoms like strong urge to urinate, painful urination, frequent need to urinate, urine leakage, abnormal urine colour (urine looks cloudy), pressure in the lower pelvis (pelvic pain), foul-smell while urinating, pain in the side (flank) and /or fever (above 100 degrees F).
Urinary tract infections are classified based on effected area –
• Pyelonephritis (infection is in kidney) – patients may have back or side pain, high fever, nausea and vomiting
• Cystitis (infection is in bladder) – patients may feel pressure in pelvic, lower abdominal pain, frequent or painful urination and even can notice blood in urine.
• Urethritis (infection is in urethra) – patients may feel inflammations while urinating and may have urine leakage.
UTIs are common in women than men. UTIs are very common, happening in 1 out of 5 females, it may also occur to males, older adults and kids. Usually, female have a shorter urethra, so this less distance to bladder helps bacteria to reach easily and cause infection. Having sex for the first time or with new sexual partner increases the risk of infection. Using birth control measures like diaphragms and spermicidal agents increase the risk of UTIs. Menopause, diabetes, kidney stones, urinary tract problems also contribute to the risk factors.
Urinalysis is done to analyse a urine sample for testing white and red blood cells or bacteria. Urine culture is done to determine the type of bacteria in urine. If you have recurrent UTIs, the other tests required to diagnose infections are ultrasound, cystoscopy and CT scan or MRI.
Customarily antibiotics, depending on type of infecting bacteria, are the primary treatment for urinary tract infections. Usually, UTI symptoms fade off within a few days of treatment, but do not fail to continue modification as prescribed. Pain relievers also may be prescribed depending on infection.
If not treated on time UTIs can lead to severe complications like permanent kidney damage, repeated infections and sepsis (a life-threatening complication).
Prevention
• Drink plenty of fluids, particularly water to flush bacteria from the urinary tract. Drinking more water dilutes the urine and reduces the risk of recurring cystitis.
• After having sex immediately empty your bladder which aid in flushing out bacteria and drink lots of water.
• As per study increased intake of vitamin C reduces the risk of UTIs. It makes urine acidic, which help to kill bacteria that may cause infection.
• Do not hold urine for too long.
• Avoid hypothetically irritating feminine products like deodorant sprays, douches and powders, especially in the genital area.
• If you are prone to UTIs then avoid diaphragms, unlubricated condoms, spermicide.
Dr Ramesh
Altius Hospital
No. 6/63, 59th Cross, 4th Block, Rajajinagar,
Entrance (Opp.)to, MEI Polytechnic, Bangalore -10.
Ph : 080 23151873 Mobile : Phone: +91 8882799799
Email : info@altiushospital.com
http://www.altiushospital.com