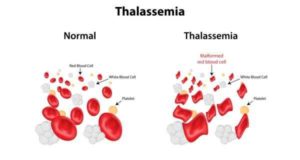
 Is Thalassemia a serious health burden for India? Thalassemia is a genetically inherited blood disorder that has one of the highest incidence rates in India, with more than 10,000 children being born with Thalassemia per year making India officially the Thalassemia capital of the world. Thalassemia is a serious health burden for India – reports claim that we have more than 1 lakh people with Thalassemia major undergoing treatment and more than 4 crore people being carriers of the Thalassemia gene in India. Thalassemia is purely a genetically transmitted disease. It is advisable to those who want to enter motherhood to opt for genetic testing and counseling to understand what health risks, if any, they may be passing on to their child and how to make a conscious choice when planning for a baby.
Is Thalassemia a serious health burden for India? Thalassemia is a genetically inherited blood disorder that has one of the highest incidence rates in India, with more than 10,000 children being born with Thalassemia per year making India officially the Thalassemia capital of the world. Thalassemia is a serious health burden for India – reports claim that we have more than 1 lakh people with Thalassemia major undergoing treatment and more than 4 crore people being carriers of the Thalassemia gene in India. Thalassemia is purely a genetically transmitted disease. It is advisable to those who want to enter motherhood to opt for genetic testing and counseling to understand what health risks, if any, they may be passing on to their child and how to make a conscious choice when planning for a baby.
Parents play an integral role in determining the fate of their child, not only through their developing years but also in terms of what kind of genes they pass on. Over 10,000 children with thalassemia major are born in India per year. There is an undeniable need to focus on prevention strategies to reduce the transmission of the Thalassemia gene from parent to offspring. Living with the disease can dramatically impact the quality of life of the child and the family as we do not have an easy way of curing Thalassemia without significant risks. Bone marrow transplant is the only known cure for Thalassemia however this is not a viable option for all patients.
70% of affected patients may not be ideal candidate for bone marrow transplant due to older age or because they do not have a matched sibling. Thalassemia drastically reduces a child’s ability to function normally in society as they have to constantly be aware of their health. Children with Thalassemia can suffer from a host of health consequences such as excess iron in the body, swollen liver/spleen, hormonal deficiency, cardiac problems and weak bones among others. Not only do these children have to undergo lifelong blood transfusion therapies to make up for the lack of hemoglobin production in their bodies, they will also have to undergo treatments for Thalassemia associated disorders. It is an expensive, timeconsuming and exhausting affair to constantly be fighting for life. The number of complications as well as the financial and emotional costs increase with time. The family will also have to take extra measures to encourage psycho-social growth of the child and integrate him into society.
 The reason why Thalassemia has reached such epidemic proportions is two-fold. People earlier were either unaware about how the disease is transmitted and unwittingly bore a child with Thalassemia or they were aware of the possibilities of producing a child with Thalassemia and did not consciously consider the impact of the disorder on the quality of life of the child.
The reason why Thalassemia has reached such epidemic proportions is two-fold. People earlier were either unaware about how the disease is transmitted and unwittingly bore a child with Thalassemia or they were aware of the possibilities of producing a child with Thalassemia and did not consciously consider the impact of the disorder on the quality of life of the child.
The custom of marrying among relatives has also contributed to increased incidence of many genetic diseases in India including Thalassemia. The carrier status of thalassemia can be very easily established by a simple and non-expensive test known as haemoglobin electrophoresis which is widely available. Developed countries such as Italy where thalassemia was once very common have virtually eliminated thalassemia form their country by raising awareness and by making thalassemia carrier state screening mandatory.
An individual can either be a carrier of the Thalassemia gene or a Thalassemia patient. We all have two genes representing the genetic code for production of beta globin protein, absence of this protein leads to beta-thalassemia. Individuals where only one of the two genes are defective are carriers of Thalassemia gene. They are not affected clinically but remain as silent carriers and are also known as Thalassemia minor. When two individuals who have the Thalassemia gene produce an offspring, there is a high likelihood that the child will be born with Thalassemia major (where both the gene copies are defective) – which is the most severe form of the disorder and requires lifelong treatment. A subset are affected with slightly less severe form of the disease called Thalassemia intermedia which deals a softer blow on the child’s health, but the child will still suffer from anemia, weakness and potential liver/spleen dysfunction or failure before eventually may end up having regular blood transfusions and severity is very variable among the intermedia group.
 While it is clear that living with the disease greatly impacts the quality of a patient’s life, there are also roadblocks in terms of accessibility and costs of treatment. The benefits of tackling the disease at its roots far outweigh the pains of having to live with the disease. Here is where pre-marital screening and counseling contributes greatly to help couples make educated choices when it is time to conceive. Even if both partners are carriers still the Thalassemia can be prevented by special tests on the fetus during early pregnancy. The government in India must make efforts to introduce pre-marital genetic counseling and screening for Thalassemia mandatory for all couples and ensure basic knowledge about inherited genetic disorders are part of school curriculum. The onus is also on doctors to educate their patients about thalassemia on how the disease spreads and how the patient can make educated choices when/if they choose to have children in the future.
While it is clear that living with the disease greatly impacts the quality of a patient’s life, there are also roadblocks in terms of accessibility and costs of treatment. The benefits of tackling the disease at its roots far outweigh the pains of having to live with the disease. Here is where pre-marital screening and counseling contributes greatly to help couples make educated choices when it is time to conceive. Even if both partners are carriers still the Thalassemia can be prevented by special tests on the fetus during early pregnancy. The government in India must make efforts to introduce pre-marital genetic counseling and screening for Thalassemia mandatory for all couples and ensure basic knowledge about inherited genetic disorders are part of school curriculum. The onus is also on doctors to educate their patients about thalassemia on how the disease spreads and how the patient can make educated choices when/if they choose to have children in the future.

Dr. Stalin Ramprakash
Consultant, Paediatric Haematology, Oncology & BMT
Aster CMI Hospital, Hebbal,
Bengaluru- 560092
Ph: 080-43420100











