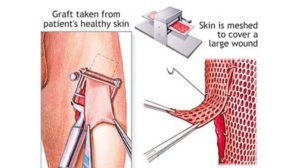
Skin donation and skin banking is gaining prominence in the medical field as it has high benefit to the mankind. But the concept of skin donation after death is not new and the first skin bank was established in USA around 1950.
Skin Grafting procedure to treat burns and other wounds began as early as 800 B.C. Modern organ transplant procedures began in the early 1900s. In 1936, an Ukranian doctor Yu Yu Voronoy transplanted the first human kidney, using an organ from a deceased donor. The transplant was successful but Voronoy’s patient died shortly after as a result of organ rejection which was the cause for many failures in the early years of transplant technology.
The first successful kidney transplant by surgeons at Boston’s Peter Bent Brigham Hospital in 1954 worked because the recipient and donor were genetically identical twins. In 1960, British immunologist Peter Medawar won the Nobel Prize for his studies in acquired immune tolerance that lead to the development of anti-rejection drugs, allowing patients to receive organs from non-identical donors. The awareness for organ transplants like Kidney, Liver, Pancreas and eye has lead to the increased number of such transplants. Apart from blood and these organs , banked human tissues include:
1. Bone- frozen, freeze-dried, and de-mineralized
2. Corneas
3. Heart valves
4. Tendons
5. Skin
6. Hematopoietic tissues, bone marrow and cord blood.
7. Dura mater, ear ossicles, and cartilage.
| Important dates in the history of tissue Donation | |
| 1878 | First successful human-to-human bone transplant. |
| 1881 | First use of skin from a cadaver used for burn victim. |
| 1908 | First knee transplant from a cadaver. |
| 1949 | First bone- and tissue-processing and storage facility opened at the U.S. Naval Medical Center. |
| 1955 | First heart valve and artery transplants |
| 1976 | The American Association of Tissue Banks was established to set safety, ethical, inspection and accreditation standards. |
| 1989 | There are more than 20,000 tissue transplants per year. |
| 1995 | The number of tissue transplants each year reaches 500,000. |
| 1998 | Federal regulations require hospitals to notify local organ-procurement organisations when someone dies so they can ask the family if it would like to donate organs and tissues. |
Importance of skin donation:
The skin is the largest organ in the body. The functions of skin are
1. Skin acts as a barrier to bacterial invasion.
2. Prevents loss of body proteins and fluids
3. As an organ in temperature regulation.
Early burn wound closure is crucial for survival of patients with large burn wounds. Burn wound infection leading to systemic sepsis is the single most major cause of death in burn patients. Burn wound is a devastating trauma that affects the patients physically, psychologically, socially and economically. Patients with burn size up to 40-50% of total body surface area (TBSA) can usually be treated with auto grafts obtained from the unburnt areas of the patient. Auto graft will be insufficient in larger burn size or in patients without available donor areas. Hence the skin donors are very essential to save the lives of burn injury patients.
Skin Autograft donors can be : Living or Cadaver
1 .Living skin donation has the following features:
1. The donor has to undergo investigations for preoperative evaluation.
2. A surgical procedure under suitable anesthesia for harvest of graft.
3. Hospitalization is required for at least 2 days.
4. Donor site healing time and wound site pain of about 10-14 days.
5. Only 15 to 20% of total body surface can be harvested at a time.
6. The other alternative is to procure split thickness skin grafts from a cadaver donor and preserve them for use in future.
2 .Cadaver skin donation:
The concept of skin donation after death is not new and the first skin bank was established in USA around 1950. The benefits of use of autograft on full thickness burn wounds are
1. Effective control of protein and fluid loss from wounds.
2. Reversal of hyper metabolic state with improvement in nutritional status.
3. Augmentation of immunological response.
4. Control of wound infection and improvement in the wound bed making it ready for acceptance of precious skin auto grafts.
5. Immediate pain relief and general feeling of well being.
6. Excellent biological wound cover till the auto graft donor sites become ready for taking of skin again.
7. Important information regarding skin donation
8. Only a thin layer of skin from thighs and back is taken.
9. No disfigurement! No bleeding!
10. No blood matching is required.
11. Can donate skin up to 24 hrs following death of a person.
12. Helpline numbers are available.
13. Hospital’s doctor’s team will come within 2 hours of your call.
14. Skin will be harvested in about 45 minutes.
Who can donate skin?
 A person above 18 yrs of age, not having transmissible diseases like hepatitis, HIV, skin cancer or skin diseases can donate skin. Even an old person with wrinkled skin can also donate. Skin can be harvested up to 12 hours and with precautions even up to 24 hours after death if the body is kept in a cold storage. The skin quality must be good.
A person above 18 yrs of age, not having transmissible diseases like hepatitis, HIV, skin cancer or skin diseases can donate skin. Even an old person with wrinkled skin can also donate. Skin can be harvested up to 12 hours and with precautions even up to 24 hours after death if the body is kept in a cold storage. The skin quality must be good.
Who cannot donate skin?
Persons harboring transmissible infections such as Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C and HIV cannot donate skin. Skin from people suffering from skin cancer, persons who died of septicemia with damaged skin e.g. scleroderma, pemphigus should not be taken. The skin must be free of tattoos.
Why skin donation?
Skin is usually donated to patients suffering from burn injuries, diabetic wounds and to trauma patients requiring coverage of raw areas. It covers the exposed body and prevents the entry of bacteria. Controls the loss of protein, heat and fluid from the body. Gives the patient enough time to develop his own skin available for covering the wounds. The applied skin acts as a biological dressing for the patient.
Stored Donor skin graft is useful in the following clinical situations
Poor general condition of patient with high risk for surgical procedures. Insufficient auto graft donor sites especially in patients with major burn injuries. Risk of increase in the size of wound due to addition of donor site wound to the actual burn area and its associated complications unhealthy recipient bed and general status of the patient when skin graft procedure may be associated with graft loss. When the expected duration for harvesting skin graft from the same donor sites is more than 3 weeks.
Legal requirements:
1. Death certificate from the competent authority
2. Consent form signed by the next of kin.
Xenografts (from other species e.g. pig-skin) are not commercially available in many countries. Biosynthetic skin substitutes (artificial skin) are extremely expensive and unaffordable for most of the burnt patients in developing countries. Their availability is also uncertain. The only cost effective and definite alternative is skin allograft obtained from a human donor and stored in Skin Banks. The efficacy of skin allograft in the management of burn wound was realized in 1881.
These skin substitutes provide temporary but long term wound closure, with potential to save life of patients with large burn. The skin allograft transplant differs from organ transplantation as the skin grafts are used to provide temporary long term protection and are not expected to survive in the recipient permanently as transplanted organ. This means that neither ABO blood group nor HLA matching is required for allograft skin transplantation. So any human being can be a donor for anyone else.
Organization of a Skin Bank:
Permission for establishing a skin bank with procurement of deceased donor skin allograft has to be obtained from appropriate authority of the government. Though skin is an organ, split thickness skin graft (STSG) is considered as a tissue. The following protocols are prepared.
1. Defining the eligibility criteria.
2. Communication and response details.
3. Readiness of equipment and response team.
4. Skin procurement protocol.
5. Transport equipment & protocol.
6. Deposition and information routine.
7. Homograft and serological processing protocol.
8. Storage method and quality control.
9. Procedure for requisition and disbursement of homograft.
10. Record keeping.
Protocol preparation in relation to the following criteria
1. Response to donation call
2. Procurement of deceased donor skin allograft with consent of the next-of-kin.
3. Microbiological studies.
4. Viability testing of donated skin.
5. Preservation methods.
6. Awareness campaign
An ongoing awareness program is essential for success of the skin donation campaign. Brochures, posters, flip charts and power point presentations, educational films, articles in print media, television interviews and radio talks, guest lectures in social service organizations and in educational Institutions on a regular basis will create an awareness among the public. Development of burn survivor community and their interaction with the public will be more effective.
The skin bank team consists of: counselor, contact person,response team including surgeon, assistant, helper, supervising consultant, Microbiologist or biochemist, record keeper
Skin graft procurement:
Standard protocol for graft harvesting methods has to be followed. With shortest delay possible after death (it can be procured up to 24 hours after death if the body is preserved in cold storage) skin should be harvested. Prolonged delay may cause bacterial and fungal colonization of the donor skin.
1. The procedure takes about one hour and conducted with aseptic precautions in operation theater.
2. Skin is harvested from both thighs and back of the deceased person.
3. There is no bleeding as blood circulation stops at death.
4. The thighs are covered with dressing before handing over the body to relatives.
5. About 10 cc of blood of the deceased is collected at the same time for serological testing.
6. The grafts are transported to the skin bank in Phosphate buffered saline in glass containers placed in ice box along-with blood sample for serology and the microbiologist is informed.
7. Counseling responsibility is by the consultants and residents of department of surgery.
8. Extend the counseling outside the hospital in the community as well.
9. Participation of voluntary organizations may be useful in skin donation awareness.
Microbiological analysis:
1. Microbiological analysis of deceased donor skin allograft is carried out on regular basis
2. Appropriate protocols must be followed in the donor area cleaning.
3. Protocol for graft harvesting techniques.
Equipment required:
1. Instruments for skin graft procurement including dermatome.
2. Refrigerator and Incubator.
3. Ultra-cool refrigerator for -70 degree C temperature.
4. Laminar flow cabinet with air conditioners.
5. Universal power supply.
6. Laboratory articles, reagents, chemicals, furniture.
7. The cost of consumables for procuring skin donation including the cost of serological testing has to be worked up.
Storage and disbursement of homograft:
 Initially the harvested skin is stored in 50% Glycerol for two hours at 4-6 degrees C for 2 hours. Then it is checked for any infection and the put in 85% Glycerol for 3 hours at 33 degrees C in a shaking incubator. Then the skin is kept in a freezer at 8 degrees C for 4-6 weeks until the serological reports are available. After 4-6 weeks the graft is transferred to a bio-safety cabinet and made into smaller uniform strips. The skin is then preserved in 85 per cent glycerol in a temperature of 4 degrees and it is ready for use. The treated cadaveric skin has a shelf-life of four to five years. The stored graft is checked every 3 months for bacterial or fungal infections. The stored graft is used for treating patients with damaged skin due to burns or injuries.
Initially the harvested skin is stored in 50% Glycerol for two hours at 4-6 degrees C for 2 hours. Then it is checked for any infection and the put in 85% Glycerol for 3 hours at 33 degrees C in a shaking incubator. Then the skin is kept in a freezer at 8 degrees C for 4-6 weeks until the serological reports are available. After 4-6 weeks the graft is transferred to a bio-safety cabinet and made into smaller uniform strips. The skin is then preserved in 85 per cent glycerol in a temperature of 4 degrees and it is ready for use. The treated cadaveric skin has a shelf-life of four to five years. The stored graft is checked every 3 months for bacterial or fungal infections. The stored graft is used for treating patients with damaged skin due to burns or injuries.
The future of Skin banking:
1. Augment the awareness in the medical fraternity regarding skin donation.
2. Participation of teaching institutions, peripheral hospitals and private hospitals for counseling
3. Participation of voluntary organizations in the awareness campaign.
4. The facility for skin banking should ideally be available in every medical college hospital
5. Several collection centers can be affiliated to each skin bank facility.
6. Training in standardized graft procurement protocol can be provided to available personnel.
7. Establishment of Tissue Bank Association to ensure the quality in functioning of skin banks.
Further research to improve the quality of skin is necessary. Recently introduced Glyaderm (preserved acellular dermal substitute), a science of Bi-layered skin restoration technology will benefit the patients in future.
Also Read: ORGAN DONATION-INDIA STRUGGLING WITH SHORTAGE OF ORGANS FOR TRANSPLANTATION

Dr.N.Mariappan- Chennai.
Consultant Plastic surgeon
Mob:9901043568