Kidney infections, also known as pyelonephritis, are serious conditions that require prompt medical attention. Recognizing the signs of a kidney infection can aid in prompt diagnosis and management, hence preventing complications.
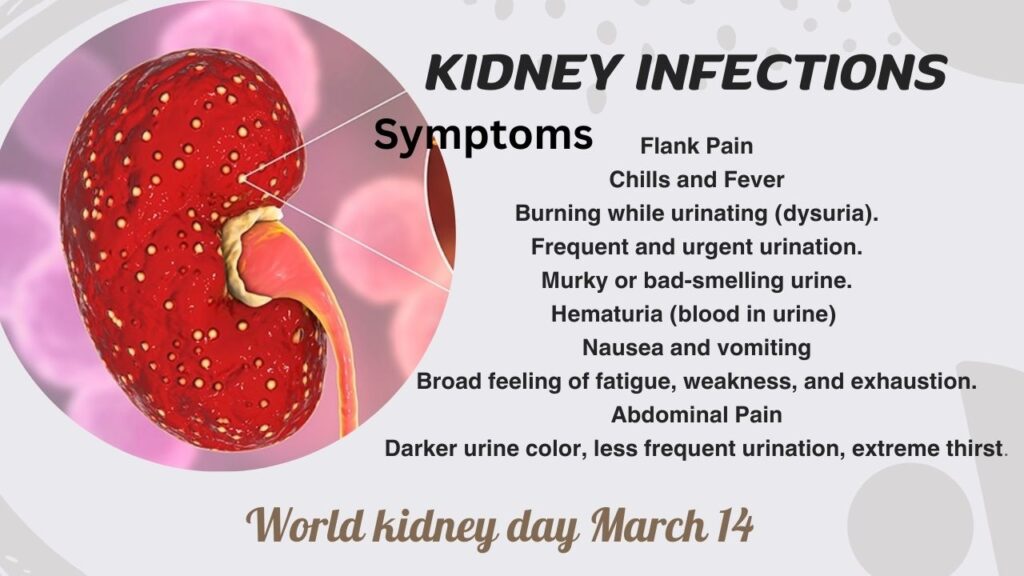

Symptoms of Kidney infection
• Pain in the flanks, usually on one side of the back, is one of the main signs of a kidney infection. This discomfort frequently gets worse with movement or pressure. It might be subtle and chronic or severe and strong.
• Chills and fever are frequent concomitant signs of kidney infections. Shivering or feeling too chilly might be symptoms of an increased temperature caused by the body’s immunological reaction to the infection.
• Urinary symptoms associated with kidney infections often include burning while urinating (dysuria), frequent and urgent urination, and murky or bad-smelling urine. Hematuria, or the presence of blood in the urine, can also occur in certain people.
• When an infection worsens, people may feel sick to their stomachs and vomit. This is usually because of how the body reacts to the illness and the pain it causes.
• A broad feeling of fatigue, weakness, and exhaustion are examples of systemic symptoms that can result from kidney infections. The body’s attempt to combat the infection and the effects of bacterial toxins may be the cause of these symptoms.
• Some kidney infections might cause abdominal pain or discomfort in addition to flank pain. This lower abdominal pain can be localized or diffuse, and it might be misdiagnosed as other gastrointestinal problems.
• Dehydration symptoms or a discernible drop in urine production could occur in severe kidney infections. Urine that is darker in color, less frequent urination, or extreme thirst are some signs of this.
Treatment and Management
It is essential to treat kidney infections as soon as possible in order to avoid consequences like kidney damage or bloodstream infections. Antibiotics are usually used in treatment to get rid of the bacterial infection. It may be required to administer intravenous fluids and painkillers in cases of acute pain or dehydration.
If you think you may have a kidney infection, you should definitely see a doctor, especially if your symptoms are severe or getting worse. Serious consequences and a longer recovery time can result from delayed treatment.
Prevention
Following proper hygiene, drinking plenty of water, and treating urinary tract infections (UTIs) as soon as possible are all important steps in preventing kidney infections. Kidney infections can also be lowered by safe sex practices and avoiding extended urine retention.
In summary, prompt action and therapy of a kidney infection depend on the ability to identify its symptoms. Seek medical assistance right once if you suffer any of the aforementioned symptoms, especially if they worsen over time or persist. Most kidney infections can be successfully treated with the right care, which lowers the chance of complications and encourages a quick recovery.


Dr AK Gadpayle
Head Department of Medicine – Sharda Hospital