How much do you know about your eyes? Eyes are the most precious of our sense organs. They contribute greatly to one’s learning capacities right since childhood. Good vision contributes greatly to the strength of health & wits.
- Importance of Eyes
The school going years are the formative years for determining one’s physical, intellectual & behavioral development. Any problem in the vision during the formative years can hamper the intellectual development, maturity & performance of a person in his future life.
Children usually don’t complain of defective vision. They may not even be aware of their problems. They adjust to the poor eyesight by moving closer to the black board, holding the books closer to their eyes, squeezing the eyes and even avoiding work requiring visual concentration.
This evades early detection. Timely detection of these problems and their correction by spectacles (or surgery) can tremendously improve the child’s potential during his formative years. Visual impairment can be a drag in the life of a child, his family and the society. Periodic screening of children helps in early identification of visual defects and prescriptions/use of corrective spectacles.
- What is an eye?
Which part of your body lets you read your favourite book, check out a rainbow, and see a football heading your way? Which part lets you cry when you’re sad and makes tears to protect itself? Which part has muscles that adjust to let you focus on things that are close up or far away? If you guessed the eye, you’re right!
Your eyes are at work from the moment you wake up to the moment you close them to go to sleep. They take in tons of information about the world around you — shapes, colours, movements, and more. Then they send the information to your brain for processing so the brain knows what’s going on outside of your body.
You can see that the eye is pretty amazing. So, come on let’s take a tour of its many parts.
- The Parts of the Eye
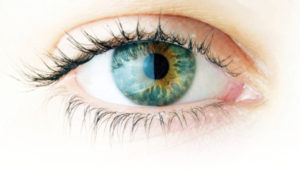
The cornea is a round, transparent dome that acts as the outer window of the eye. It is the structure that focuses the light that enters the eye. The coloured part of the eye is known as iris. The iris lies between the cornea and the crystalline lens. The color is due to the presence of a pigment The basic iris colors are blue, green and brown. Majority of humans have varying shades of these colours. It is composed of connective tissues and smooth muscle fibres.
- About the Eye
The composition of the iris enables it to dilate or contract the pupil, which in turn controls the amount of light that falls on the retina.
The lens is that part of the human eye that is located immediately behind the iris. Its role is to focus the light and move towards the retina.
The retina is the innermost layer of the eye. It consists of nerve tissue that senses the tight entering the eye. Its function is to send impulses through the optic nerve back to the brain, where it gets translated into the images that we see.
The sclera is the whitish, opaque part of the eye, which is connected to the cornea. Its role is to provide protection and meet the purpose of attachment for the extraocular muscles that enables eye to move.
- How do our eyes work?
Every day we see things with our eyes. We see the sky, trees, cats, birds and the faces of our friends, but how do we see all that?
Light enters our eye through the pupil. The cornea, at the front of our eye, bends the light. The light passes through the lens to the retina. It then focuses on the retina, like a little picture of whatever we are looking at, but it is upside down! Nerve cells in the retina send that “Image” to our brain. The brain has the ability to interpret that the image is upside down and we see it right side up.
- Eye nutrition and Eye Health
Like any other part of your body, your eyes also need looking after. Because eyes are so precious, we need to really take care of them.
Eating fruits, vegetables and fish is good not only for your body but also for your eyes. Food like green leafy vegetables, spinach, papaya, corn, green peas and egg yolks are good for ocular health. Apricots are good antioxidants and help in protecting the eye lens.
Multi vitamins especially Vitamin A, also help in reviving eye nutritional balance. Most types of milk are also fortified with Vitamin A. Vitamin A is essential to proper functioning of the retina. It also helps prevent night blindness by helping the eye to adapt between bright light and darkness.
Common Eye Diseases
Several eye problems are often seen in newborns and children, some of which are no cause for concern and will self-correct naturally. In either case, any apparent abnormality should be checked by a doctor, as it could be the sign of a more serious condition.
Blocked tear ducts are a condition seen in 2 to 4 percent of newborns and of these cases, 90 percent resolve naturally.
Amblyopia, or lazy eye as it is more commonly known, is a common condition that affects one out of every 40 children. To correct this condition the child will probably need to wear an eye patch on the normal eye.
Although cataracts are much more common in adults, children can be born with this condition or develop it later. Cataracts must be removed as soon as possible irrespective of the age.
Another common eye problem often seen in infants and children is strabismus, or crossed eyes. Surgery to correct strabismus is generally quick and painless and the child can usually resume normal activities within a day or two.
More common in school-age children, infectious conjunctivitis, or pink eye, is one of the most common eye conditions, due to its highly contagious nature. Treatment of pink eye can depend on which type it is. Bacterial conjunctivitis is treated with antibiotics in a drop or ointment. Viral conjunctivitis cannot be treated with antibiotics and will usually clear up on its own in just a few days.
For eye problems contact
Narayana Nethralaya, Bangalore, Karnataka, Telephone no: +91-80-66121300-305
Email : info@narayananethralaya.com, info@nnmail.org, Website : www.narayananethralaya.org