Atherosclerosis can be prevented through basic lifestyle changes from a young age There is a need for awareness around the health complications of atherosclerosis and the importance of managing vitals.
There is a rise in the incidence and prevalence of atherosclerotic diseases such as coronary heart disease, stroke, etc. Both men and women are susceptible to this condition and the rate of hospitalization due to the complications caused by atherosclerosis is about 2 to 4 times higher in Indians than other ethnic groups. There is a need to raise awareness about the condition and the need for timely diagnosis.
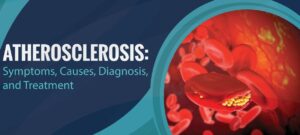
Atherosclerosis causes hardening of the arteries and is a common disorder. In this condition, fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up in the walls of arteries. This leads to the formation of hard structures called plaques. Over time, the plaques can block the arteries and cause problems such as coronary artery disease or CAD.
What is Atherosclerosis?
Atherosclerosis is a silent condition and the symptoms do not show up until the arteries are severely narrowed or blocked. If left undiagnosed, it can lead to medical emergencies such as heart attacks or a stroke. In some people, it can show up as angina or chest pain/discomfort. This happens when the heart muscle doesn’t receive enough oxygen-rich blood. Many people mistaken the pain for indigestion. Some of the risk factors include diabetes, high blood pressure and cholesterol, smoking, obesity, lack of physical activity and a sedentary lifestyle, and even a family history of atherosclerosis.
Most of these factors can be managed from a young age. It is also important to avoid undue stress and get regular check-ups done to keep vitals under control. It is not possible to reverse the hardening of the arteries once it has occurred. However, one should make lifestyle changes and treat high cholesterol levels to prevent the condition from becoming worse. In people who develop complications due to atherosclerosis over time, a surgery may be needed. Angioplasty is one such intervention that can help restore and improve blood flow.
In angioplasty, a long, thin tube (catheter) is inserted into the narrowed part of the artery. A thin wire mesh (stent) mounted on a deflated balloon is then passed through the catheter to the narrowed area. The balloon is inflated; compressing the deposits against the artery walls and leaving expanded stent embedded in the artery. Drug-eluting stents release medication to help heal the stressed arteries post procedure. Few drug-eluting stents are USFDA approved and well-studied for safe use in patients with complications such as diabetes, high bleeding risk or in patients who might have to interrupt medication a month after angioplasty.
Tips to prevent atherosclerosis and heart problems
1. Consume a low-sodium diet with no more than 5 gm of sodium chloride in a day.
2. Minimize the consumption of trans fats found in hydrogenated oils or vanaspati ghee.
3. They reduce the good HDL cholesterol and increase the bad LDL cholesterol. Avoid eating out as much as possible since the food in most restaurants and hotels has high amounts of trans fats.
4. Avoid refined carbohydrates such as bread, pasta or even white sugar. Replace them with options like whole grain flour, healthy green cereals and oatmeal.
5. Exercise regularly – at least for about 30 minutes a day—as it has numerous benefits for the heart.
6. Quit smoking and restrict alcohol.

Dr Naresh Kumar Goyal
Senior Director Interventional Cardiology
BLK Hospital, New Delhi