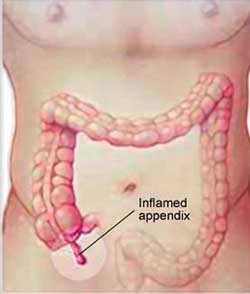
Appendicitis is a disorder in which appendix gets inflamed and filled with pus. Appendix is a finger-shaped pouch that projects out from colon on the lower right side of stomach. This small structure has no purpose, but that doesn’t mean it can’t create a problems.
The focal symptom of appendicitis is pain that normally starts around bellybutton and then moves to lower right stomach. The ache of appendicitis generally surges over a period of 6 to 12 hrs, and ultimately turn out to be very acute. Anybody can develop appendicitis, but most often attacks people of 10 to 30 age. The standard management for appendicitis is surgical removal of the appendix.
Symptoms
Symptoms may change eventually:
• Initially it starts aching around bellybutton that usually shifts to lower right stomach.
• When swelling feasts to close tissues, the pain may go sharper and become severe.
• Ultimately, the pain inclines to settle in lower right stomach — near appendix at McBurney point. A point is about halfway between bellybutton and the top of right pelvic bone.
But the position of pain may fluctuate, based on age and position of appendix. Young children or pregnant, specifically, may have pain at different places.
What makes pain worse?
If gentle pressure to the area is applied, it hurts and feel tender. When a pressure is realised, particularly if done abruptly, pain will worsen (rebound tenderness). Patient face acute when coughed, while walking or make other shaking movements. This is mostly true if the swollen appendix is touching the peritoneum — the silk-like membrane that lines the inner stomach wall and encloses the intestines. The pain may decrease if patient lie on one side and pull their knees up toward their chest.
Symptoms other than pain
In addition to pain, patients may have one or more of the following:
- Nausea and sometimes vomiting
- Loss of appetite
- A low-grade fever that starts after other symptoms appear
- Constipation
- An inability to pass gas
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal swelling
Causes
The cause of appendicitis is not always clear. Sometimes it’s the outcome of:
• An obstacle. Food waste or a hard stool can get stuck in an orifice of the cavity that runs the length of appendix.
• An infection. It is caused due to gastrointestinal viral infection, or it may be due to other inflammation.
In both cases, bacteria may enter rapidly, making the appendix inflamed and filled with pus. If not treated punctually, appendix is probable to rupture.
When to get medical advice?
Children are more vulnerable to ruptured appendix. Children may not always have usual symptoms. So, it’s best not to neglect abdominal pain. Even if stomach ache isn’t acute, call doctor for advice.
Older adults also have a higher chance of getting ruptured appendix, perhaps because of delay in consulting doctors.
Tests and diagnosis
The pain may change over time, so diagnosing can may be difficult. In addition, stomach pain can also arise due to other health problems. Other conditions with abdominal pain that may resemble appendicitis are:
- Ectopic pregnancy – occurs outside the lining of uterus
- A right-sided ovarian cyst may cause pain.
- Kidney stone. Sporadically, a stone from the right kidney will pass to ureter, runs from the kidney to the bladder, and get stuck. This causes substantial pain.
- Crohn’s disease. Chronic swelling of the digestive tract, also can mimic appendicitis.
Diagnosis
When gentle pressure on the painful area is suddenly released, pain will go worse if the adjacent peritoneum is inflamed. Other signs include stomach inflexibility and stiffness of abdominal muscles for pressure.
Oher procedures:
• Blood test – To check for a high white blood cell count, which may indicate an infection.
• Urine test.
• X-ray or ultrasound scan.
Universally, a computerized tomography (CT) scan is used for confirming a diagnosis. A CT scan is used to get a more comprehensive view of internal organs.
Complications
When appendix ruptures, patient may suddenly feel better. But soon afterward, entire abdomen may become distended with gas and fluid and will likely feel tight, hard and tender to the touch. And experience pain throughout belly, but may not have the severe pain. Further, patient may not be able to pass gas or bowel because of the swelling. Other symptoms are fever, thirst and a low urine output. Peritonitis is a medical emergency.
Sometimes, infection and the seepage of intestinal contents may form an abscess, a walled-off area of infection. The abscess may be as small as a walnut or as large as a grapefruit. Regardless of its size, it requires treatment before the abscess itself perforates, causing peritonitis.
Treatments and drugs
Appendicitis treatment requires surgical removal of appendix. Surgeon may perform traditional open surgery (using a single abdominal incision), or laparoscopic surgery, (only a few small abdominal incisions).
In general, laparoscopic surgery allows to recover faster and heal with less scarring. But if your appendix has ruptured and infection has spread beyond then there is necessary for larger incision to clean the abdominal cavity.
Dr. Chalapathy
Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences & Research Centre,
#82, Nallurahalli, Whitefield, Bangalore – 560 066
+91-80-49069000, +91-80-28413382, +91-80-28410871/2/3/4