Routine Immunization during COVID 19 is very necessary. Due to the wide spread of COVID 19 across the states, there is a potential threat that multiple routine immunization activities could be wedged partially or entirely.
 World has been challenged with an unparalleled health emergency in the form of COVID 19. (caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome corona virus 2, SARS-CoV-2). The ongoing corona virus pandemic has continually subjected the existing healthcare systems to unprecedented burdens and has shifted the entire focus of organizations and world health forums towards measurement of containment of spread of this deadly virus.
World has been challenged with an unparalleled health emergency in the form of COVID 19. (caused by Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome corona virus 2, SARS-CoV-2). The ongoing corona virus pandemic has continually subjected the existing healthcare systems to unprecedented burdens and has shifted the entire focus of organizations and world health forums towards measurement of containment of spread of this deadly virus.
COVID-19 is an infectious disease that primarily spreads through droplets of saliva or discharge from the nose when an infected person coughs or sneezes. Henceforth, its transmission occurs either by direct contact with the infected persons or through indirect contact of the contaminated environmental surfaces. Treatment deficiencies like absence of vaccine or a recognized medicinal regimen, makes it obligatory to rely upon the recommended measures like social distancing, isolation, quarantine etc.
Potential threat to routine immunization :
Overriding burden on existing health care system along with legislative decisions like nationwide lockdown, has impacted the routine immunization services beyond anticipation. Immunization against vaccine preventable diseases (VPDs) is recognized as a life savior intervention. Continual immunization practices resulted in eradication of fatal diseases like smallpox. Ministry of Health and Family Welfare provides free vaccination against 12 vaccine preventable diseases under the umbrella of Universal Immunization Program.
In a country like India, with humongous birth group, Routine Immunization services are carried out majorly through RI sessions, by a designated ANM(vaccinator). Country conducts approximately 120 Lac RI Sessions to cover the cohort of 260 Lac of children and 290 Lac of pregnant women annually. Due to the wide spread of COVID 19 across the states, there is a potential threat that multiple routine immunization activities could be wedged partially or entirely. Apart from acknowledged contributors like healthcare encumbrance, restricted movements etc., community unwillingness and apprehension can be further associated with staggered RI activities.
The compromised immunization services, even for shorter periods, will result in increased numbers of unvaccinated cohort and create a potential of outbreak prone to vaccine preventable diseases (VPDs) such as measles and diphtheria. Such VPD outbreaks may result in increased morbidity and mortality predominantly in young infants, which may put additional strain on health workers and health systems, which is already overwrought by the COVID-19 response.
Importance of immunization during Covid-19 :
On 26th March 2020, WHO issued a guideline highlighting the importance of Immunization during Covid-19 where it was stated that “where feasible immunization delivery strategies may need to be adapted and should be conducted under safe conditions, without undue harm to health workers, caregivers and the community. The temporary suspension of mass vaccination campaigns was also suggested.
Prioritizing other health programs during an emergency situation like Covid-19 is extremely challenging for the system. Parallel incidence in Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) has occurred in past when during Ebola outbreak in country, more children lost life due to measles (6500), than Ebola outbreaks (2264). With major focus on the rapid spread of the novel corona virus, there is a fear in health experts, that delay of scheduled vaccine doses can possibly result in heightened vulnerability towards vaccine preventable diseases outbreak.
Home confinement, fear, movement of informal migratory population towards their native places has all contributed towards the marginal coverage. A Benefit-risk analysis among routine childhood immunization and risk of SARS-CoV-2 infections during the Covid-19 pandemic in Africa was conducted by a team of researcher at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine (LSHTM) which says that for every one excess Covid-19 death attributable to SARS-CoV-2 infections acquired during routine vaccination clinic visits, there could be 140 (37 – 549) deaths in children prevented by sustaining routine childhood immunization in Africa. Also, as per another study, it was observed that the death rate was as lowered as 4.28/million in countries with BCG Immunization programs compared to 40/million in countries without such a program.
Road Ahead:
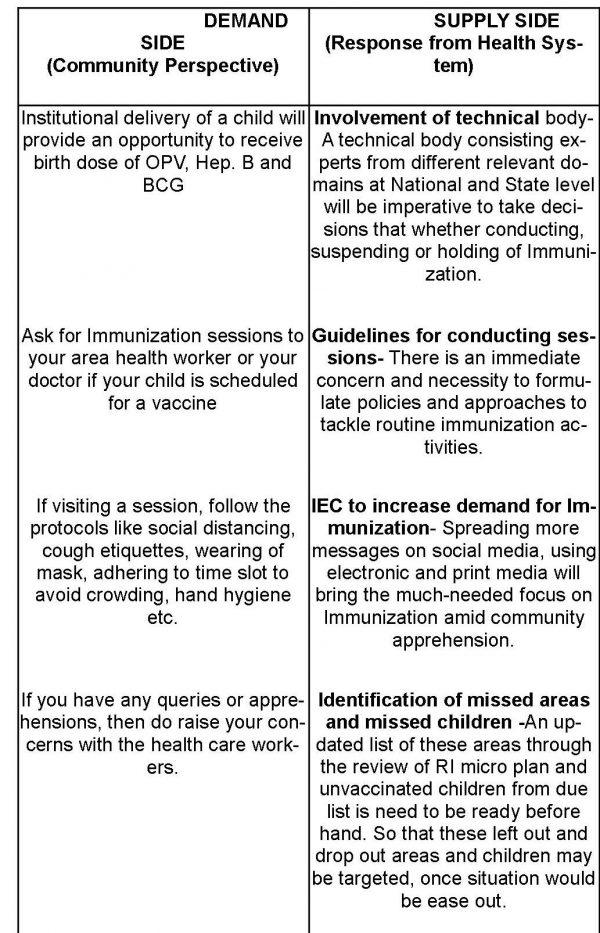
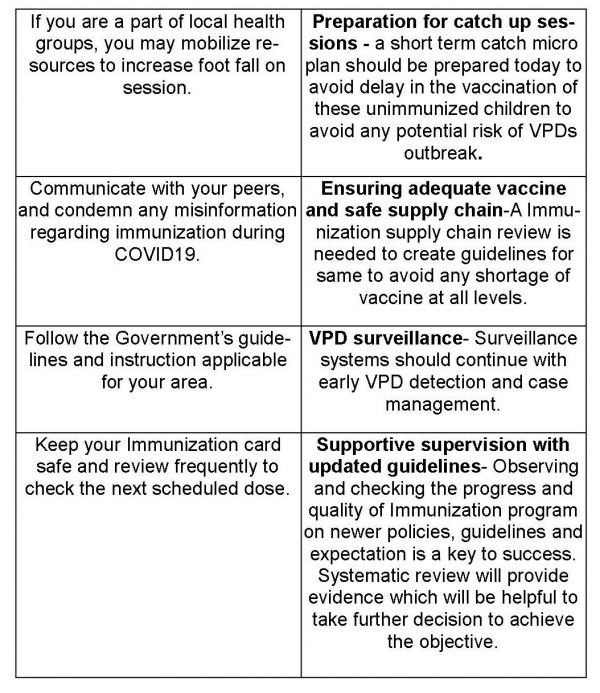
With the ongoing pandemic, as social distancing is becoming a way of life, there is a pre-requisite to plan immunization activities concerning the health of caregivers as well as the beneficiaries. We should work towards protecting our self at least from the identified diseases, while we wait for protection from the unrevealed. The need of the hour is to streamline collective efforts from both the demand as well as supply side of routine immunization.
*The views expressed in the article are author’s personal and by no means depict any endorsement from NIHFW or any associated departments or organizations

Dr. Snehil – Coordinator & Team Lead
National Cold Chain & Vaccine Management Resource Centre
The National Institute of Health & Family Welfare
Phone: +91 11 2616 5959 (Ext: 237), Mob : +91 9690007821
Email: snehil.me@gmail.com, snehil@nihfw.org