Down syndrome in children cannot be cured medically. Yet there is a medical aid for children with down syndrome at early interventions, starting in infancy. Children with Down syndrome have a dissimilar facial look.

Down syndrome is a hereditary disarray that causes mental retardation and other illness. It is a mixture of physical abnormalities and psychological retardation which has a genetic defect in chromosome pair 21. It is called so because of the British doctor John Langdon Down, who first explored it in 1866. The condition fluctuates in severity, so struggle for development may vary from mild to serious. Around 1 in 800 to 1 in 1,000 babies are born with this chaos. Life expectancy among adults with Down syndrome is about 55 years approximately.
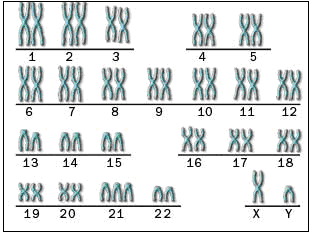 There are 23 chromosomes in egg and sperm cells of human. The rest of cells usually contain 23 pairs of chromosomes — one from father and one from mother. Kids with Down syndrome typically have 3 copies of chromosome 21 — known as trisomy 21 — in the place of two copies.
There are 23 chromosomes in egg and sperm cells of human. The rest of cells usually contain 23 pairs of chromosomes — one from father and one from mother. Kids with Down syndrome typically have 3 copies of chromosome 21 — known as trisomy 21 — in the place of two copies.
Human cells usually has 23 pairs of chromosomes. One chromosome in each pair comes from father, the other from mother. Down syndrome is caused by 3 types of abnormal cell division linking 21st chromosome. All 3 defects and its outcome is extra genetic material from chromosome 21, which causes Down syndrome. The 3 genetic variations are:
1. Trisomy 21: Above 90 % of Down syndrome are the result of trisomy 21. A infant with trisomy 21 has 3 copies of chromosome 21 — in the place of the typical 2 copies. is caused by irregular cell division while sperm or the egg cell develops.
2. Mosaic Down syndrome: It is a rare form, where infants have some cells with an extra copy of chromosome 21, but not all. This mosaic of normal and abnormal cells is caused by abnormal cell division after fertilization.
3. Translocation Down syndrome: It also occurs when part of chromosome 21 gets attached to a different chromosome, before or at conception.
Signs and Symptoms
Children with Down syndrome have a dissimilar facial look. Though all patients do not have the same features, some general characteristics that can be listed are:
1. Flattened facial features
2. Protruding tongue
3. Small head
4. Upward slanting eyes, unusual for the child’s ethnic group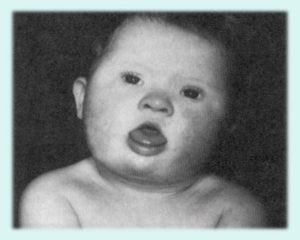
5. Unusually shaped ears
Children with Down syndrome may also have:
1. Poor muscle tone
2. Broad, short hands with a single crease in the palm
3. Relatively short fingers
4. Excessive flexibility
5. Baby born with this illness may be of normal size, but usually their development is slow and stay behind in growth compared to than other children of same age. They are also mental retarded to some extent, typically from mild to moderate
Is it inherited?
Most of the time it is not inherited. They’re caused by a error in cell division while egg, sperm or embryo development. The diagnosis is based on clinical appearance and genetic testing.
Screening tests during pregnancy
Diverse screening tests can aid in identifying the probability of developing Down syndrome. Conventionally, blood tests — such as quad screen or maternal serum alpha-fetoprotein (MSAFP) test — were advised around the 16th week of pregnancy
First-trimester screening is done in two parts:
Ultrasound: It is used to gauge a specific region on the back of a baby’s neck, called nuchal translucency screening test. Babies with certain abnormalities have a propensity of accumulating more fluid in this tissue than otherwise usual.
Blood tests: To measure the levels of pregnancy associated plasma protein A (PAPP-A) and a hormone called as human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG).
Diagnostic tests for newborns
After birth, the primary diagnosis depends on the baby’s appearance. If child exhibit some or all of the features of illness, it is advised for chromosomal karyotype test. To analyse extra chromosome 21 present in all or some of the cells.
Complications
1. Heart defects: Roughly 50 % of Down syndrome children some type of heart defects are been found. It may be life-threatening and may need surgery at early childhood.
2. Infectious diseases: Due of defect in their immune system, they are more vulnerable to infectious illness. In particular, risk of pneumonia is much higher that others.
3. Dementia: Later in life, people with Down syndrome have a greatly increased risk of dementia. Signs and symptoms of dementia often appear before age 40 in people with Down syndrome.
4. Other problems. Down syndrome may also be connected with a multiple illness, including gastrointestinal blockage, thyroid problems, hearing loss or poor vision.
Treatment
Down syndrome cannot be cured medically. Yet, there is a medical aid for children with down syndrome at early interventions, starting in infancy.
Prevention
There’s no root to prevent Down syndrome. Indeed Down syndrome infected child can typically do most things that any young child can do, such as walking, talking, dressing and being toilet-trained. Nevertheless, they usually take more time to learn the same. At present, there are more prospects than earlier which includes schooling, jobs and social relationships.

Dr. C. Sharath Kumar
Director and Chief Fertility Surgeon
Mediwave I.V.F & Fertility Research Hospital
Mysore-570 021
Phone: 0821-2444441/3265002











